The Ultimate Game Localization Guide for Global Impact

If you have ever played a game that felt as if it truly understood your culture, your humor, or even your slang, you already know the power of great localization.
In today’s global gaming market, success is no longer limited by borders but depends on how well your game resonates with players worldwide. In 2025, there are over 3.32 billion gamers around the world, representing nearly half of the global population and reflecting continuous year-over-year growth.
This guide shows you how to localize your game for global impact, reach millions of new players, and grow your brand worldwide. Let’s dive in.
Game Localization and Game Translation
Game translation and localization are closely related but far from identical. While both involve adapting a game for players who speak different languages, translation focuses primarily on converting text accurately, whereas localization goes deeper, ensuring the game feels natural, culturally relevant, and engaging for the target audience.
Key Differences Between Translation and Localization:
| Aspect | Game Translation | Game Localization |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Converts text from one language to another | Adapts the game to feel native in another region |
| Scope | Text-focused | Cultural, linguistic, and technical adaptation |
| Content Covered | Dialogue, menus, tutorials, UI text, subtitles, item descriptions | Tone, humor, symbols, cultural references, gameplay context |
| Cultural Adaptation | Not included | Fully considered and adapted |
| Technical Adjustments | Minimal or none | Fonts, RTL text, spacing, voiceover syncing |
| Player Experience | Accurate and clear | Natural, immersive, and culturally relevant |
| Goal | Preserve original meaning. | Make players feel the game was made for them. |
Many developers compare translation vs localization, wondering which one matters more. In reality, translation is only the foundation. Localization is what transforms the game into an experience players feel was made for them. If you only translate, your game becomes understandable. If you localize, your game becomes unforgettable.
Localization teams often use creative adaptation techniques similar to transcreation, especially when dealing with jokes, idioms, or emotional storylines that do not translate directly. This combination ensures both accuracy and emotional impact.
Benefits of Video Game Localization
The global video game market is expected to generate around $188.28 billion in revenue in 2025, growing about 3.4% year over year. This includes spending on mobile, console, and PC games, with mobile gaming still the largest segment (~$103 billion), followed by console (~$45.9 billion) and PC (~$39.9 billion) revenues.
Venturing into global markets without localization is like releasing half a game. Here is how localization can transform your success:
1. A bigger global audience
Making your game available in multiple languages allows you to reach far more players than a single-language release. Countries like Japan, South Korea, Germany, France, Brazil, and China have strong gaming cultures where localized games consistently outperform non-localized ones.
2. Higher downloads and revenue
Players are more likely to buy or download a game that speaks their language. The conversion rate increases dramatically, especially in markets where English proficiency is low. For studios, this means improved ROI on development, marketing, and player acquisition.
3. Stronger emotional engagement
Games are emotional journeys. When storylines, jokes, and quests feel familiar and culturally relevant, players feel seen, understood, and immersed. This increases playtime, loyalty, and long-term retention.
4. Competitive advantage
With numerous games launching every week, localization can set your product apart. Studios that ignore localization often face localization challenges later, especially when trying to retrofit content instead of planning from the start.
5. Brand trust and community growth
Gamers who feel valued become loyal fans. They share content, join communities, and help promote the game through word of mouth, reviews, and social media. Localized games often benefit from stronger communities in nonnative markets.
Game Localization Examples
To show why localization matters, here are a few standout examples:
1. Genshin Impact
Genshin Impact became a global success by focusing on deep localization instead of simple translation. The game features separate voiceovers for each supported language, with dialogue adapted to match cultural tone, emotion, and storytelling styles.
In addition, UI spacing, narrative details, and regional references were carefully adjusted to suit different languages and audiences. This made the game feel native to players around the world, increasing immersion and global appeal.
2. The Witcher 3
The Witcher 3 is renowned for its storytelling and strong localization approach. Dialogue, humor, and cultural elements were carefully reshaped to suit different regions rather than being translated literally.
Idioms, jokes, and folklore references were adapted to feel natural in each language, helping players connect with the world and characters as if the game were originally written for them.
3. PUBG Mobile

PUBG expanded its global reach by tailoring the game experience to different regions. The developers introduced cultural skins, region-specific events, and language-optimized interfaces to better connect with local players.
Even item names and in-game terminology were adapted to match what felt familiar and relatable in each market, helping PUBG build a massive and diverse worldwide audience.
4. Animal Crossing
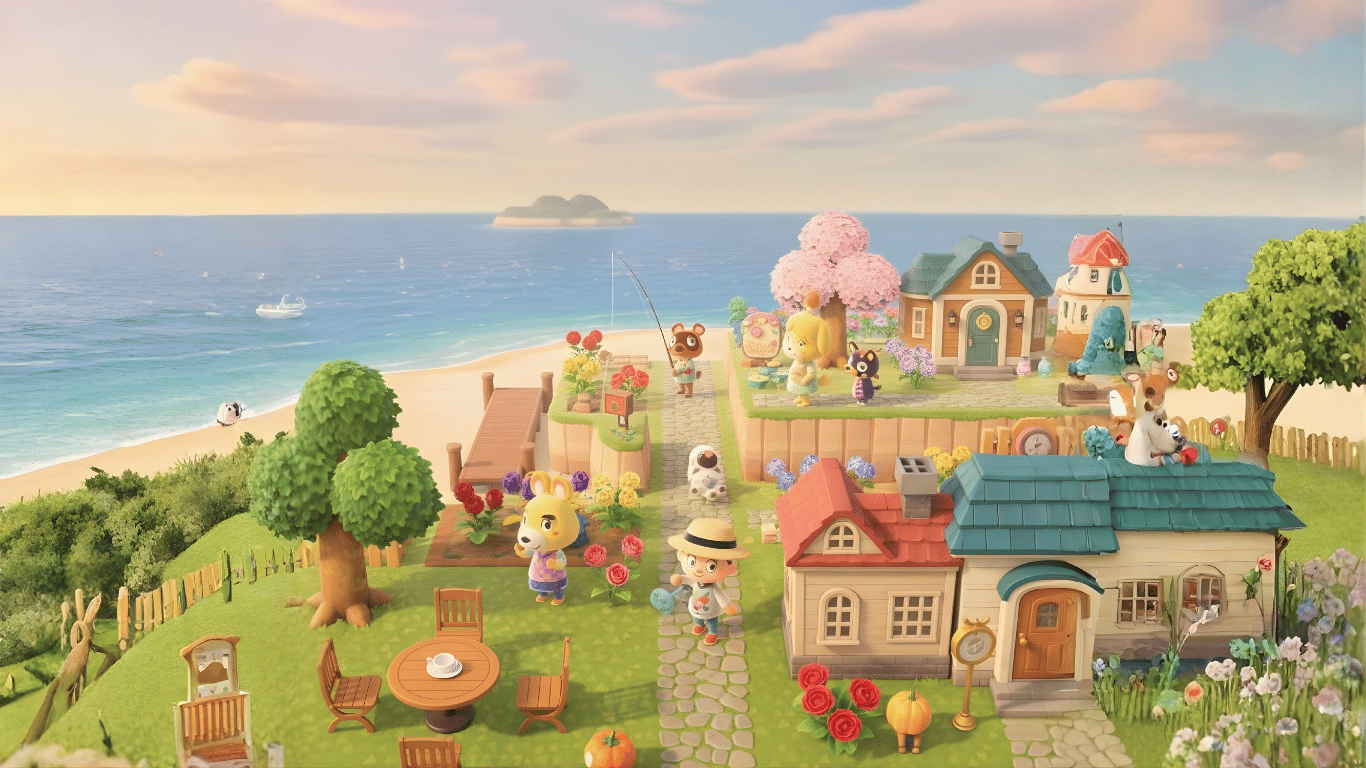

Animal Crossing is a standout example of cultural adaptation done right. Seasonal events, holidays, and festivities are adjusted by region so they align with local calendars and traditions.
Food items, references, and small cultural details are also adapted, helping players feel at home and deeply connected to the game’s world.
These examples show that localization is not just about replacing text. It is about understanding the emotion behind the content and recreating the experience authentically.
Game Localization Challenges
Localizing a game can be complex. Here are the most common challenges developers face:
1. Cultural mismatch
Jokes, symbols, body language, or character designs may unintentionally offend or confuse players from other cultures. This is a major source of localization mistakes and must be addressed early.
2. Technical limitations
Text expansion, character encoding, UI constraints, gendered languages, and right-to-left rendering can all create unexpected development hurdles.
3. Inconsistent terminology
Games often have hundreds of items, story arcs, and gameplay mechanics. Without proper glossaries or style guides, inconsistencies can break immersion.
4. Voiceover complexity
Matching lip sync, keeping character personalities intact, and maintaining audio quality require skilled teams and high-quality equipment.
5. Last-minute localization
When localization is treated as an afterthought, rushed deadlines often lead to errors, delays, and poor player experience. This mistake is one reason why global businesses fail when entering new markets.
6. Budget constraints
Quality localization requires writers, translators, editors, voice actors, QA testers, and sometimes cultural consultants. Cutting corners may save money initially but can hurt global reputation later.
Tips to Optimize the Game Localization Process
To overcome these challenges and ensure smooth localization, follow these optimization strategies:
1. Plan for localization from day one.
Build your game with localization in mind. Use variable placeholders, avoid hard-coded text, and design UI layouts that can adapt to text expansion. Early planning reduces cost and time later.
2. Create style guides and glossaries.
Document tone, character personalities, world rules, item names, terminology, and consistency guidelines. This helps translators maintain accuracy across languages.
3. Use native-speaking translators with a gaming background.
Nothing beats native cultural understanding. Professional linguists who play games can adapt humor, slang, and emotion while keeping technical accuracy intact.
4. Invest in linguistic QA.
Test the game in each localized language, not just for grammar but also for gameplay issues, UI overlaps, and cultural alignment.
5. Keep developers and translators connected.
Strong communication ensures translators understand the context behind text strings, emotional tone, and gameplay mechanics.
6. Leverage localized marketing.
Support your localization efforts with matching social media content, trailers, and descriptions. This helps amplify your global reach and SEO performance with external linking keywords.
7. Combine expertise
Many teams now take a hybrid approach similar to concepts explored in Human vs. AI Translation, using AI to generate drafts and human experts to polish cultural authenticity.
Step-by-Step Guide to Game Localization
Here is a comprehensive roadmap to help studios navigate the entire localization process:
Step 1: Assess your target markets
Identify countries with strong gaming demand that align with your genre. Consider market size, culture fit, spending behavior, and regional platform popularity.
Step 2: Prepare your content
Extract all translatable assets, including dialogue, tutorials, menus, subtitles, UI strings, item descriptions, cinematic text, marketing copy, and metadata. Organize them clearly for the localization team.
Step 3: Set style guidelines
Define tone, writing style, character backgrounds, and terminology. Provide world-building notes and visual references when possible. This minimizes inconsistencies later.
Step 4: Choose your localization team
Depending on budget and scope, choose a localization partner, freelance gaming translators, or an internal team. Ensure they understand both gaming terminology and cultural nuances.
Step 5: Translate and adapt content
Translation begins here, but remember, adaptation is equally important. Humor, quests, references, and emotional beats should feel natural in each language.
Step 6: Localize audio and voiceovers
Record voiceovers with native actors. Maintain character integrity, pacing, and emotional tone. Check lip sync and timing if cutscenes or animations are voice driven.
Step 7: Implement localized content
Developers integrate localized text and audio into the game. This step often reveals layout issues, text overflow, spacing conflicts, or missing assets.
Step 8: Linguistic and functional QA
Test for tone consistency, grammar, UI alignment, gameplay clarity, and cultural sensitivity. QA ensures local players receive a polished experience.
Step 9: Localize metadata and marketing assets
Store descriptions, trailers, promotional banners, and app store content need cultural adaptation too. This boosts discoverability and global revenue.
Step 10: Launch and update regularly
Release localized versions and keep updating content. Player feedback is vital for maintaining long-term engagement across regions.
Conclusion
Game localization is not just a technical step; it is a strategy that shapes your global identity. By investing in types of translation, cultural nuance, and localized storytelling, you can build worldwide communities that feel connected to your game.
If you want to reach global audiences, connect with diverse communities, and grow your brand worldwide, now is the perfect time to prioritize localization. The world is playing, and your game might be the next big hit waiting to be discovered.
FAQ
How can you start a career in game localization?
Breaking into game localization usually requires a mix of language skills, cultural knowledge, and gaming experience. To get started:
- Build strong proficiency in at least two languages
- Understand gaming terminology and genres
- Learn localization tools (CAT tools, QA platforms)
- Create a portfolio with translated or localized game content
- Apply to localization agencies, game studios, or freelance platforms
Having hands-on experience with games is a major advantage.
What is game localization?
Game localization is the process of adapting a video game for players in different regions and languages. It goes beyond simple translation by adjusting cultural references, humor, symbols, visuals, and gameplay elements so the game feels natural and immersive to local audiences.
What are the responsibilities of a game localizer?
A game localizer ensures that a game delivers the same experience across different markets. Their responsibilities typically include:
- Translating in-game text, UI, and dialogue
- Adapting cultural references and idioms
- Reviewing tone, humor, and context
- Testing localized builds for linguistic and cultural accuracy
- Collaborating with developers and QA teams
What does localization mean in video games?
In video games, localization is the process of adapting a game to suit the language, culture, and regional expectations of players. It includes translation, voice-over and subtitle adjustments, cultural sensitivity changes, legal compliance, and visual adaptations, with the goal of making the game feel native to the target audience.
How much does video game localization cost?
The price of localizing a video game can differ widely based on multiple factors, such as:
- Number of languages
- Total word count
- Voice-over and audio requirements
- Level of cultural adaptation needed
- Testing and quality assurance
Small indie games may cost a few thousand dollars, while large AAA titles with multiple languages and voice acting can cost significantly more.
